Discover the Limitless Possibilities of 3D Printing
Discover the Limitless Possibilities of 3D Printing

Innovation knows no bounds and 3D printing has emerged as a groundbreaking technology that is revolutionizing various industries. From manufacturing and healthcare to fashion and art, the applications of 3D printing are vast and ever-expanding.
The Fascinating World of 3D Printing
Imagine being able to bring your imagination to life with just a few clicks. That's exactly what 3D printing offers—a way to turn virtual designs into tangible objects. Whether it's a complex architectural model or a personalized piece of jewelry, the possibilities are limited only by your creativity.
Applications of 3D Printing
The applications of 3D printing are incredibly diverse and continue to grow with each passing day. In the medical field, it has enabled the creation of custom prosthetics, implants, and even organs. Architects and engineers use it to create intricate scale models and prototypes for testing before construction begins. Artists are pushing boundaries by using this technology to create stunning sculptures and artwork.
The Advantages of 3D Printing
One of the key advantages of 3D printing is its ability to reduce waste in manufacturing processes. Traditional methods often result in excess material being discarded, whereas 3D printing allows for precise material usage, minimizing waste significantly. Additionally, it offers faster production times compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Understanding 3D Printing Basics
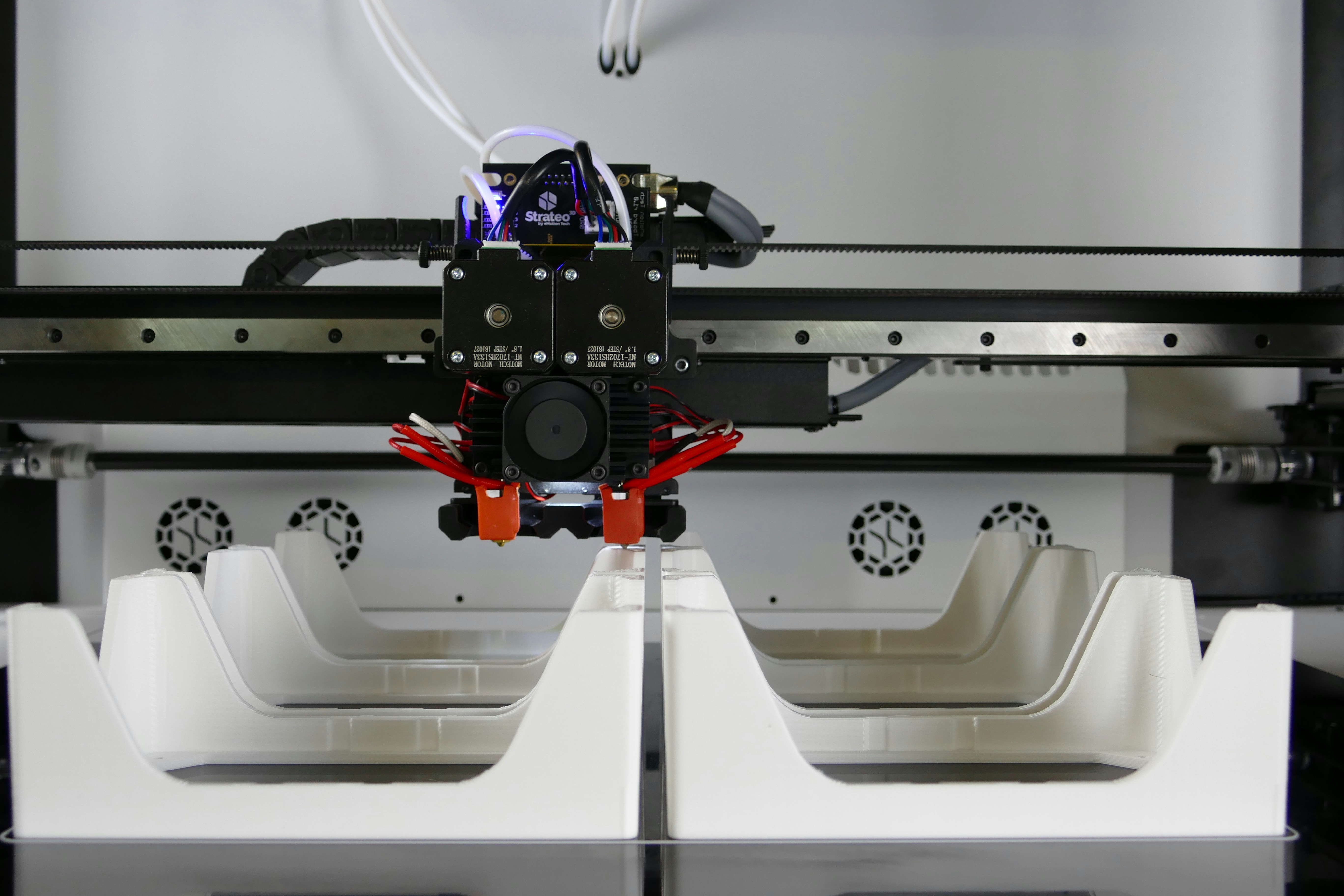
3D printing has revolutionized how we create objects, allowing us to turn digital designs into physical realities. This concept of additive manufacturing has a fascinating history from the 1980s. Over the years, various types of 3D printing technologies have emerged, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
What is 3D Printing?
At its core, 3D printing is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer. It starts with a digital model that is sliced into thin cross-sections. These slices are then sent to the 3D printer, which builds the object layer by layer until it is complete.
The history of 3D printing can be traced back to the early 1980s when Chuck Hull invented stereolithography (SLA), the first-ever 3D printing technology. Since then, advancements in technology and materials have paved the way for more sophisticated and accessible methods of 3D printing.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
Several types of 3D printing technologies are available today, each with its own advantages and applications.
One popular method is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), which extrudes melted filament through a nozzle to build up layers. FDM printers are widely used due to their affordability and versatility.
Another common technique is Stereolithography (SLA), which uses a liquid resin that hardens when exposed to light. SLA printers produce highly detailed and accurate prints, making them ideal for creating prototypes or intricate models.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is another notable technology that uses a high-powered laser to selectively fuse powdered materials together. This method allows for greater design freedom and enables the production of complex geometries.
Apart from these main technologies, there are also other methods like Digital Light Processing (DLP), Binder Jetting, and Electron Beam Melting (EBM), each with its own unique advantages and applications.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
3D printing begins with a digital model created using 3D modeling software or obtained from online repositories. This model is then sliced into thin layers using slicing software, which generates the instructions for the 3D printer.
Once the printer receives the instructions, it starts building the object layer by layer. The printer deposits or solidifies material according to the design, gradually creating a physical representation of the digital model.
Different materials can be employed in 3D printing depending on the technology used. Common filament materials include PLA and ABS, while resins are often used in SLA printers. Specialized materials like metal alloys and ceramics can also be utilized for specific applications.
Understanding the concept and history of 3D printing is crucial to grasp its potential and possibilities. By exploring different types of 3D printing technologies and how they work, we can unlock new opportunities in various industries and unleash our creativity in manufacturing previously unimaginable objects.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
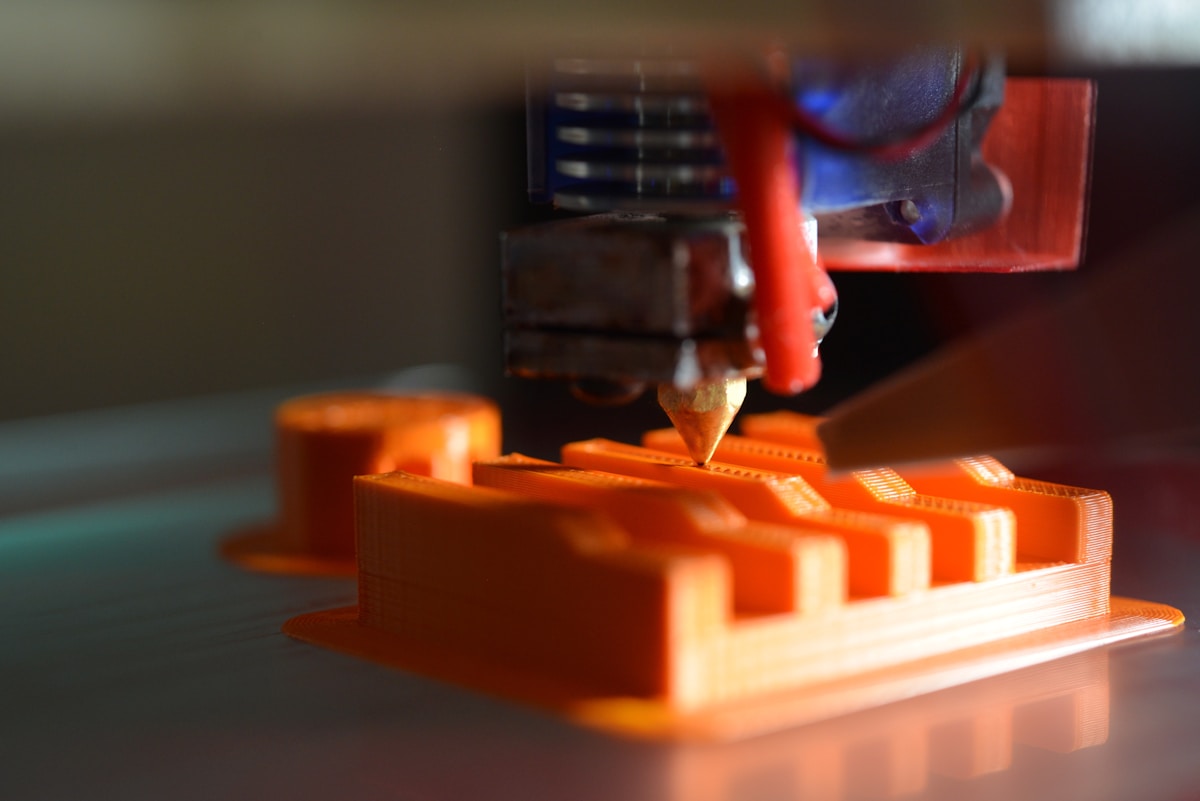
Regarding 3D printing, several different technologies enable the creation of three-dimensional objects. Each technology has its unique process and applications. Let's explore some of the most common types of 3D printing technologies.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling, or FDM, is one of the most widely used 3D printing technologies. It works by melting a thermoplastic filament and extruding it layer by layer to create an object. FDM printers are known for their affordability and ease of use, making them popular among hobbyists and small businesses.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography, or SLA, utilizes a liquid resin cured using a UV laser to create solid objects. The resin is selectively cured layer by layer until the desired object is formed. SLA printers are known for their ability to produce high-resolution prints with smooth surfaces, making them ideal for creating detailed prototypes and intricate models.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering, or SLS, involves using a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials to create solid objects selectively. This technology allows using various materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and glass. SLS printers are often used in aerospace and automotive manufacturing industries due to their ability to produce strong and durable parts.
Other Technologies
In addition to FDM, SLA, and SLS, other types of 3D printing technologies offer unique capabilities. These include Digital Light Processing (DLP), which uses a projector to cure liquid resin; Electron Beam Melting (EBM), which uses an electron beam to melt metal powder; and Binder Jetting, which involves selectively binding powder particles together using a liquid binder. Each of these technologies has its advantages and applications.
By understanding the different types of 3D printing technologies available, you can choose the one that best suits your needs and requirements. Whether you're looking to create prototypes, customized products, or even intricate art pieces, a 3D printing technology can bring your ideas to life.
3D Printing Materials
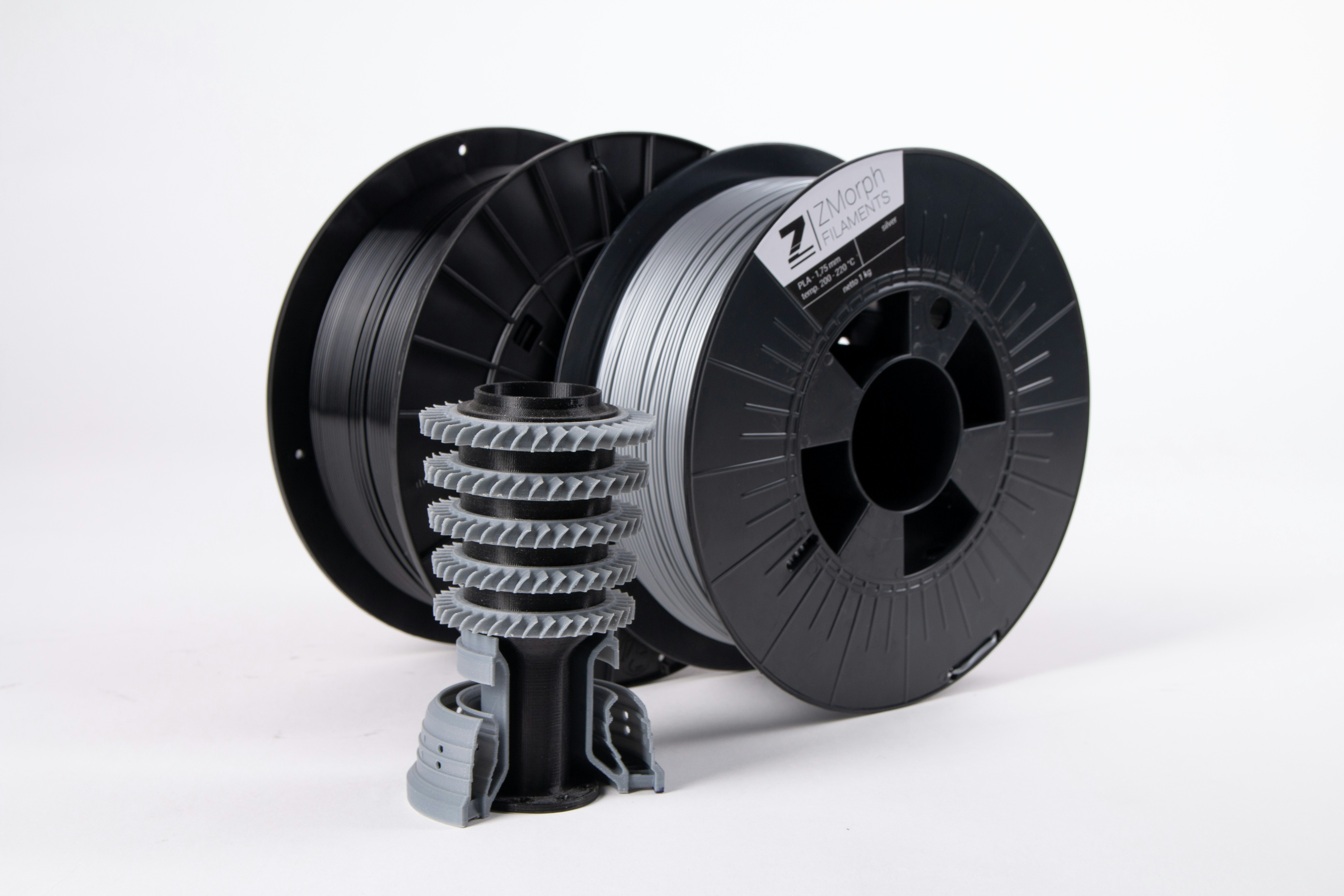

When it comes to 3D printing, the materials used are a crucial aspect of the process. There are various types of materials that can be used in 3D printing, each with its own unique properties and applications. This section will explore the different categories of materials commonly used in 3D printing.
Common Filament Materials
Filament materials are widely used in consumer-grade 3D printers that utilize Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology. The most common filament material is PLA (Polylactic Acid), derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. PLA is known for its ease of use, low cost, and environmental friendliness.
Another popular filament material is ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), which offers higher strength and durability than PLA. ABS is commonly used for functional parts or prototypes that require impact resistance.
Other common filament materials include PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol), which combines the best characteristics of both PLA and ABS and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), a flexible material suitable for creating objects with rubber-like properties.
Resin Types
Resin-based 3D printing technologies such as Stereolithography (SLA) use liquid photopolymer resins that solidify when exposed to specific wavelengths of light. These resins offer high detail and smooth surface finishes, making them ideal for creating intricate models or jewelry.
Different types of resin are available for SLA printers, including Standard Resin, which provides a balance between strength and detail; Tough Resin, designed for functional prototypes requiring impact resistance; and Flexible Resin, which offers rubber-like flexibility.
Other specialized resin types include Dental Resins for creating dental models or aligners, Castable Resins for investment casting, and High-Temperature Resins for applications requiring heat resistance.
Specialized Materials
In addition to the common filament and resin materials, a wide range of specialized materials are available for specific applications. These materials offer unique properties that expand the possibilities of 3D printing.
For example, Carbon Fiber Reinforced Filament combines PLA or ABS with carbon fiber strands, resulting in parts with exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. This material is commonly used in the aerospace or automotive industries.
Metal Filaments such as Stainless Steel or Copper-infused filaments allow for the creation of metal-like objects using FDM printers. While they do not possess the same properties as pure metal, they offer a cost-effective alternative for certain applications.
Bio-compatible resins are used in the medical field to create custom prosthetics or surgical guides. These resins are safe for contact with human tissue and can be sterilized, making them suitable for various healthcare applications.
Overall, the availability of different types of 3D printing materials allows users to select the most suitable material based on their specific needs and desired outcomes.
Creating 3D Models

Creating 3D models is an essential part of the 3D printing process. Whether you want to print a unique design or replicate an existing object, there are several ways to create 3D models.
3D Modeling Software
To create your designs from scratch, you'll need 3D modeling software. These programs allow you to design and manipulate objects in a virtual environment. Popular options include Autodesk Fusion 360, SketchUp, and Tinkercad.
Downloading Models
If you're uncomfortable with designing your models, there are numerous websites where you can download pre-made models. These sites offer a wide range of designs created by talented individuals from around the world. Some popular platforms include Thingiverse, MyMiniFactory, and Cults.
Designing from Scratch
Designing from scratch gives you the freedom to bring your imagination to life. With 3D modeling software, you can create intricate, complex designs that suit your needs. Whether a personalized gift or a prototype for a new product, designing from scratch allows for endless possibilities.
Creating your unique models requires creativity and attention to detail. Using various tools and techniques available in these software programs, you can realize your ideas.
In conclusion, creating 3D models is an exciting part of 3D printing. Whether you use existing designs or create your own from scratch, plenty of options are available to suit your needs and unleash your creativity in the fascinating world of 3D printing.
Printing and Post Processing

Printing and post-processing are crucial steps in the 3D printing process. In this section, we will explore the different aspects of printing and how to ensure a successful print.
Slicing Software
Slicing software plays a vital role in preparing your 3D model for printing. It converts your digital design into a series of instructions the printer can understand. This software allows you to customize layer height, print speed, and infill density settings.
Choosing the right slicing software for your printer and understanding its features is essential to achieve optimal results. Some popular slicing software options include Ultimaker Cura, Simplify3D, and PrusaSlicer.
Calibrating Your Printer
Before diving into printing your object, it is essential to calibrate your printer properly. Calibration ensures that the printer accurately positions the nozzle during printing, producing precise and high-quality prints.
Calibration involves adjusting parameters such as bed leveling, extruder steps per millimeter, and flow rate. Each printer may have specific calibration procedures outlined in its user manual or provided by the manufacturer.
Once you have sliced your model and calibrated your printer, it's time to start printing! Load the filament or resin into the printer according to its specifications. Set up any necessary supports or rafts if required by your model.
Start the print job using a USB connection or an SD card, depending on your printer's capabilities. Monitor the progress of the print closely to ensure there are no issues, such as filament jams or layer shifting.
Post-Processing
After successfully completing a print job, post-processing steps may be necessary to enhance the appearance or functionality of your printed object.
Common post-processing techniques include removing support structures if used during printing, sanding rough surfaces for a smoother finish, painting or applying coatings, and assembling multiple printed parts together.
Post-processing is an opportunity to add personal touches and make your 3D-printed object unique. Experiment with different techniques and materials to achieve the desired results.
Sell Your 3D Printed Creations with Strikingly

Strikingly Discover Page
When selling your 3D-printed creations, Strikingly is a platform that can help you showcase and market your products to a broader audience. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, Strikingly makes it easy to create your online 3D store.
What is Strikingly?

Strikingly Kickstart Program - We Can Build Websites For You
Strikingly is a website builder and e-commerce platform that allows individuals and businesses to create stunning websites without coding knowledge. It provides a range of templates and customization options to help you design a unique online store that reflects your brand identity.
Benefits of Using Strikingly to Sell Your 3D Print Creations
One of the major benefits of using Strikingly is its simplicity and ease of use. Whether a beginner or an experienced seller, you can quickly set up your online store with just a few clicks. The platform offers various features, such as customizable product pages, secure payment gateways, and inventory management tools to streamline your selling process.
Another advantage of using Strikingly is its responsive design. Your online store will automatically adapt to different screen sizes, ensuring customers can easily browse and purchase your 3D-printed creations from their desktops, tablets, or smartphones.

Strikingly website on a mobile device
Moreover, Strikingly provides built-in SEO tools that can help improve the visibility of your online store in search engine results. By optimizing your product descriptions, titles, and meta tags with relevant keywords like 3D printing, you can attract more organic traffic and potential buyers.
How to Create Your Own Online 3D Store with Strikingly
1. Sign up for an account on Strikingly's website.
2. Choose a template that suits the style and branding of your 3D printed creations.
3. Customize the design by adding high-quality images of your products and writing compelling descriptions.

Strikingly Product Page
5. Configure secure payment gateways to ensure smooth transactions.
6. Optimize your store for search engines by using relevant keywords throughout your website.
7. Launch your online store and promote it through social media, email marketing, and other channels.
8. Monitor your store's performance using Strikingly's analytics tools and make necessary adjustments to improve sales.
With Strikingly, you can easily create an attractive online 3D store that showcases your unique creations and attracts potential customers from around the world.
Conclusion: The Future of 3D Printing

As we look to the future, the potential for 3D printing seems limitless. This groundbreaking technology has already revolutionized various industries, and its applications continue to expand. From healthcare to aerospace, 3D printing is changing how we create and manufacture objects.
With advancements in materials and technologies, the types of 3D printing available are constantly evolving. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and other techniques offer unique benefits and cater to different needs. Understanding these options is crucial for harnessing the full potential of 3D printing.
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing holds immense promise. As technology advances, we can expect even more sophisticated printers capable of producing intricate designs with greater speed and accuracy. Materials will become more diverse, allowing for a broader range of applications.
Additionally, as more people embrace this technology, there will be an increased demand for online platforms like Strikingly, enabling individuals to sell their 3D-printed creations easily. Strikingly offers a user-friendly interface that simplifies setting up an online store dedicated to showcasing and selling unique designs.
3D printing is fascinating, and its potential is only beginning to be realized. With the ability to create customized objects, reduce waste, and revolutionize manufacturing processes, 3D printing is set to transform various industries. We can fully embrace this exciting future by staying informed about the types of 3D printing available and keeping up with technological advancements.
